Azure Arc: Extending Azure to Hybrid Environments
Servers spanning multiple datacenters, Kubernetes clusters across different cloud providers, databases remaining on-premises for compliance.
For most CTOs and IT leaders, this isn't a hypothetical scenario but daily reality. Azure Arc changes the equation by projecting all these resources into a single control plane, enabling management through Azure regardless of where workloads actually run.
- /
- Knowledge hub/
- Azure Arc: Extending Azure to Hybrid Environments
- Knowledge hub
- /Azure Arc: Extending Azure to Hybrid Environments

The Hybrid Infrastructure Challenge
Companies struggle to control and govern increasingly complex environments that extend across data centers, multiple clouds, and edge locations. Each environment possesses its own set of management tools, and new DevOps and ITOps operational models can be hard to implement across resources.
Traditional approaches force IT teams to maintain expertise across multiple platforms, each with different interfaces and operational procedures. This creates operational overhead, increases security risks, and makes consistent governance nearly impossible.
What is Azure Arc?
Azure Arc simplifies governance and management by delivering a consistent multicloud and on-premises management platform. It provides a centralized way to manage entire environments by projecting existing non-Azure and on-premises resources into Azure Resource Manager.
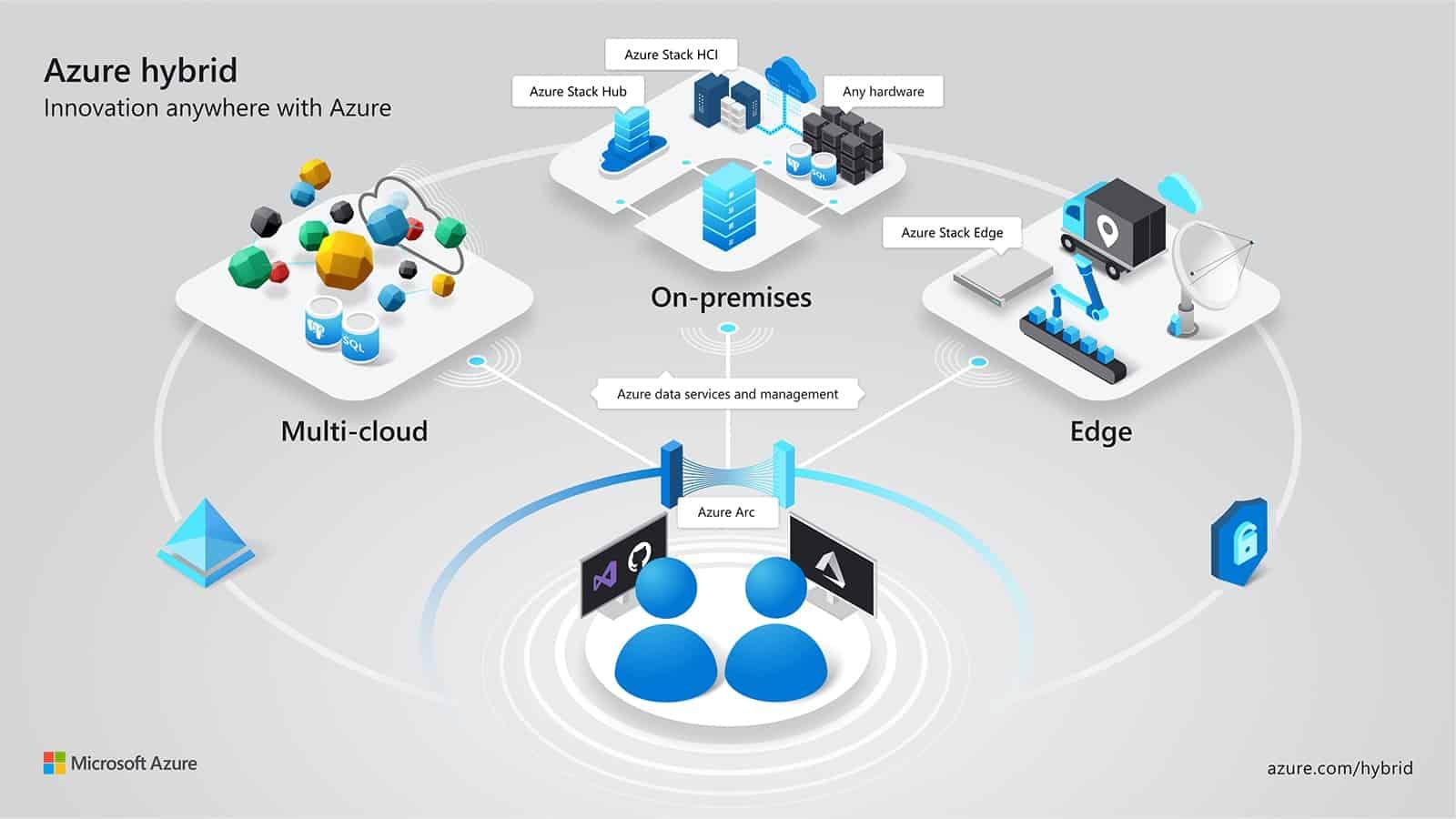
Organizations can manage virtual machines, Kubernetes clusters, and databases as if they are running in Azure. This means using familiar Azure services and management capabilities regardless of where resources live. Businesses can continue traditional ITOps while introducing DevOps practices to support new cloud native patterns. Azure Arc also allows configuring custom locations as an abstraction layer on top of Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters and cluster extensions.
What Azure Arc Can Manage
Azure Arc currently manages several resource types hosted outside of Azure.
Servers and Virtual Machines is a management capability, not a provisioning tool. It enables organizations to manage Windows and Linux physical servers and virtual machines hosted outside Azure by integrating with platforms such as Azure Local, VMware vCenter, and System Center Virtual Machine Manager.
Kubernetes Clusters running anywhere can be attached and configured, with support for multiple distributions. This allows standardizing Kubernetes management practices regardless of deployment location.
Azure Data Services can run on-premises, at the edge, and in public clouds using Kubernetes and the infrastructure of your choice. Azure Arc enables SQL Managed Instance deployment in these environments, bringing Azure's database capabilities closer to where data originates.
SQL Server instances hosted outside Azure can be connected to extend Azure services to these databases, providing unified visibility and management across your entire SQL Server estate.
Choosing the Right Azure Arc Service
Azure Arc offers different services based on your existing IT infrastructure and management needs. Understanding these distinctions helps ensure you select the approach that best suits your requirements.
Arc-enabled Servers
Azure Arc-enabled servers manages Windows and Linux physical servers and VMs hosted outside Azure, on your corporate network, or from other cloud providers. This service provides the foundation for hybrid management.
Key capabilities include assigning Azure Automanage machine configurations to audit settings and utilizing Azure Policy for compliance management. Protection comes through Microsoft Defender for Endpoint integration via Defender for Cloud, including threat detection, vulnerability management, and proactive security monitoring. Microsoft Sentinel can collect security events and correlate them with other data sources.
Configuration management uses Azure Automation for managing tasks with PowerShell and Python runbooks. Change Tracking and Inventory assesses configuration changes, while Update Management handles OS updates. Post-deployment configuration leverages supported VM extensions.
Monitoring utilizes VM insights for tracking OS performance and discovering application components. The Log Analytics agent collects performance data and events, storing it in a Log Analytics workspace. Organizations can also procure Extended Security Updates at scale for Windows Server 2012 and 2012R2 machines.
Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere and Azure Arc-enabled SCVMM have all the capabilities of Azure Arc-enabled servers, but also provide specific, additional capabilities.
Arc-enabled VMware vSphere
Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere simplifies management of hybrid IT resources distributed across VMware vSphere and Azure. Running software in Azure VMware Solution as a private cloud in Azure offers benefits not realized by operating outside Azure. For software like SQL Server and Windows Server running in Azure VMware Solution, the environment provides additional value such as free Extended Security Updates.
Capabilities include discovering VMware vSphere estate (VMs, templates, networks, datastores, clusters, hosts, resource pools) and registering resources with Azure Arc at scale. Organizations can perform various VM operations directly from Azure, such as create, resize, delete, and power cycle operations like start, stop, restart on VMware VMs consistently with Azure.
The service empowers developers and application teams to self-serve VM operations on-demand using Azure RBAC. Organizations can install the Azure Arc-connected machine agent at scale and leverage all Arc-enabled servers capabilities on VMware VMs. Businesses can browse their VMware vSphere resources in Azure, providing a single pane view for infrastructure across both environments.
Automation support includes Python, Java, JavaScript, and .NET SDKs; Terraform, ARM, Bicep templates; REST APIs, CLI, and PowerShell.
Arc-enabled System Center Virtual Machine Manager
Azure Arc-enabled System Center Virtual Machine Manager empowers System Center customers to connect their VMM environment to Azure and perform VM self-service operations from Azure portal. This solution is intended as an alternative for Azure Pack customers to perform VM self-service operations.
Capabilities include discovering and onboarding existing SCVMM managed VMs to Azure. Organizations can perform various VM lifecycle operations such as start, stop, pause, and delete VMs on SCVMM managed VMs directly from Azure. Developers and application teams can self-serve VM operations on demand using Azure RBAC.
Organizations can browse their VMM resources (VMs, templates, VM networks, and storage) in Azure, providing a single pane view. IT teams can install the Azure Arc-connected machine agents at scale and leverage all capabilities offered by Arc-enabled servers on SCVMM VMs. Businesses can build automation using Python, Java, JavaScript, and .NET SDKs; Terraform, ARM, Bicep templates; REST APIs, CLI, and PowerShell.
Azure Local
Azure Local is a hyperconverged infrastructure operating system delivered as an Azure service. This hybrid solution is designed to host virtualized Windows and Linux VM or containerized workloads and their storage. It's offered on validated hardware and connects on-premises estates to Azure, enabling cloud-based services, monitoring and management.
Azure Local comes with Azure resource bridge installed and uses the Azure Arc control plane for infrastructure and workload management, allowing you to monitor, update, and secure your Azure Local infrastructure from the Azure portal.
Capabilities include deploying and managing workloads, including VMs and Kubernetes clusters from Azure through the Azure Arc resource bridge. Organizations can manage VM lifecycle operations such as start, stop, delete from Azure control plane. Businesses can manage Kubernetes lifecycle operations such as scale, update, upgrade, and delete clusters from Azure control plane.
IT teams can install Azure connected machine agent and Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes agent on VMs and Kubernetes clusters to use Azure services like Azure Monitor and Defender for Cloud. Organizations can leverage Azure Virtual Desktop for Azure Local to deploy session hosts onto on-premises infrastructure to better meet performance or data locality requirements.
Developers and application teams can self-serve VM and Kubernetes cluster operations on demand using Azure RBAC. IT leaders can monitor, update, and secure Azure Local infrastructure and workloads across fleets of locations directly from the Azure portal. Organizations can deploy and manage static and DHCP-based logical networks on-premises to host workloads. VM image management includes Azure Marketplace integration and ability to bring images from Azure storage account and cluster shared volumes.
Decision Guide: Which Service for Your Infrastructure
Selecting the appropriate Azure Arc service depends on your machine type. The following table provides recommendations based on infrastructure:
| If your machine is a... | Connect to Azure with... |
| VMware VM (not running on AVS) | Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere (complete set of Azure capabilities) Azure Arc-enabled servers (Azure services only) |
| Azure VMware Solution VM | Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere for Azure VMware Solution |
| VM managed by System Center Virtual Machine Manager | Azure Arc-enabled SCVMM (complete set) Azure Arc-enabled servers (Azure services only) |
| Azure Local machine (including ones managed by SCVMM) | Azure Local |
| Physical server | Azure Arc-enabled servers |
| VM on another hypervisor | Azure Arc-enabled servers |
| VM on another cloud provider | Azure Arc-enabled servers |
If you're unsure, organizations can start with Azure Arc-enabled servers and add a resource bridge for additional management capabilities later. Arc-enabled servers allows connecting servers containing all types of VMs supported by other services and provides a wide range of capabilities.
Key Benefits for Enterprise Infrastructure
Azure Arc delivers consistent inventory, management, governance, and security for servers across environments through a single control plane. This eliminates the need to maintain expertise in multiple management platforms and reduces operational complexity.
Organizations can configure Azure VM extensions to use Azure management services to monitor, secure, and update servers. For Kubernetes environments, Arc manages and governs clusters at scale with zero-touch compliance and configuration using Azure Policy, ensuring security standards apply consistently regardless of where workloads run.
Businesses can run Azure data services on any Kubernetes environment as if it runs in Azure. Specifically, organizations can deploy SQL Managed Instance on-premises, at edge, and in public clouds with benefits such as upgrades, updates, security, and monitoring. Azure Arc enables an elastic scale and applies updates without any application downtime, even without continuous connection to Azure.
Organizations can perform virtual machine lifecycle and management operations for Azure Local and on-premises environments managed by VMware vCenter and System Center Virtual Machine Manager through interactive and non-interactive methods. Developers and application teams can self-serve VM operations on-demand using Azure RBAC. A unified experience viewing Arc-enabled resources is available whether using the Azure portal, the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, or Azure REST API.
Getting Started with Azure Arc
Azure Arc provides a practical approach to managing hybrid and multicloud infrastructure. For technology leaders evaluating management strategies across distributed environments, it offers consistent governance and operational control.
As of September 2025, indirectly connected mode is retired.
As a Microsoft solutions partner, Precio Fishbone helps organizations implement specific solutions aligned with their operational requirements and governance frameworks.
